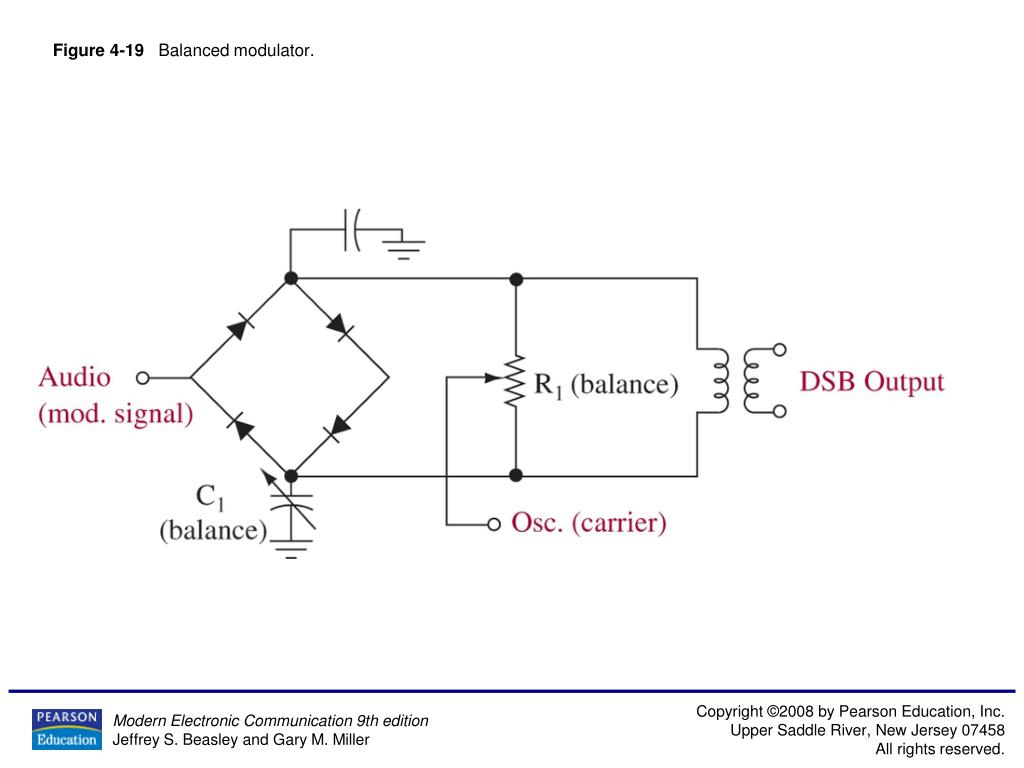
Balanced Modulators
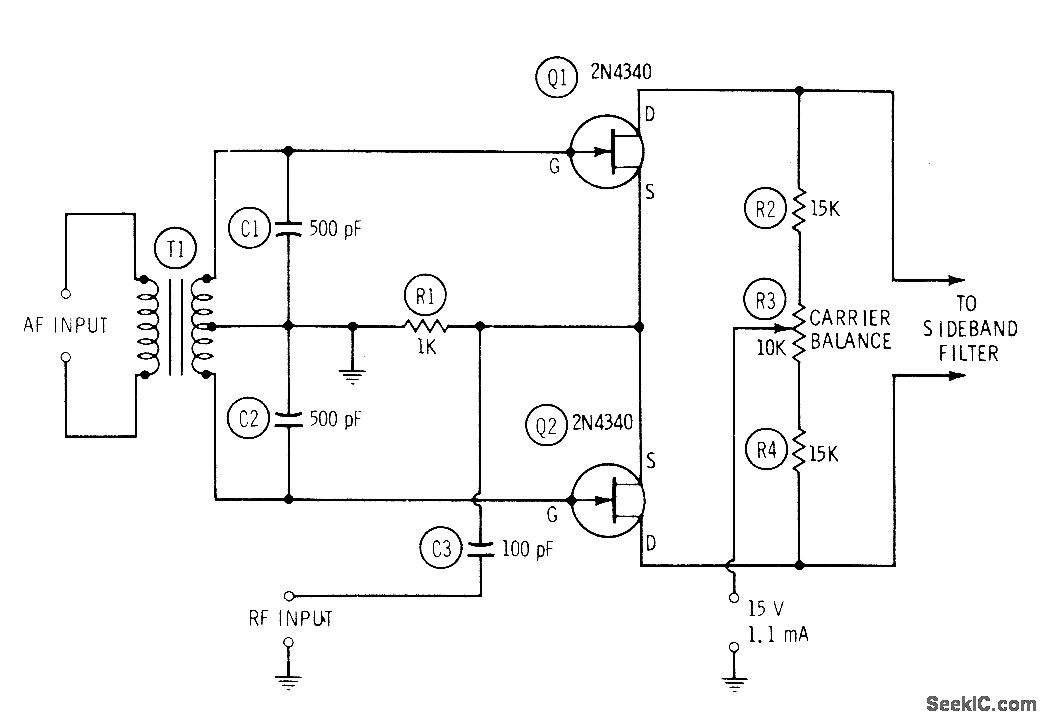
FET BALANCED MODULATOR FOR SSB under Repositorycircuits 53908 Next.gr
This circuit note discusses basic LVDT theory of operation and the design steps used to optimize the circuit shown in . Figure 1 for a chosen bandwidth, including noise analysis and component selection considerations. LVDT. Figure 1. Universal LVDT Signal Conditioning Circuit (Simplified Schematic: All Connections and Decoupling Not Shown.

Diode Modulators, April 1953 QST RF Cafe
Fig. 4 - The two common diode balanced-modulator circuits are (A) the bridge and (B) the ring. Condensers C 1, C 2, C 3 and C 4 are r.f. by-pass condensers, used to complete r.f. paths without short-circuiting the audio. Fig. 5 - A modulating signal as in (A) gives an r.f. output from a balanced modulator as in (B).
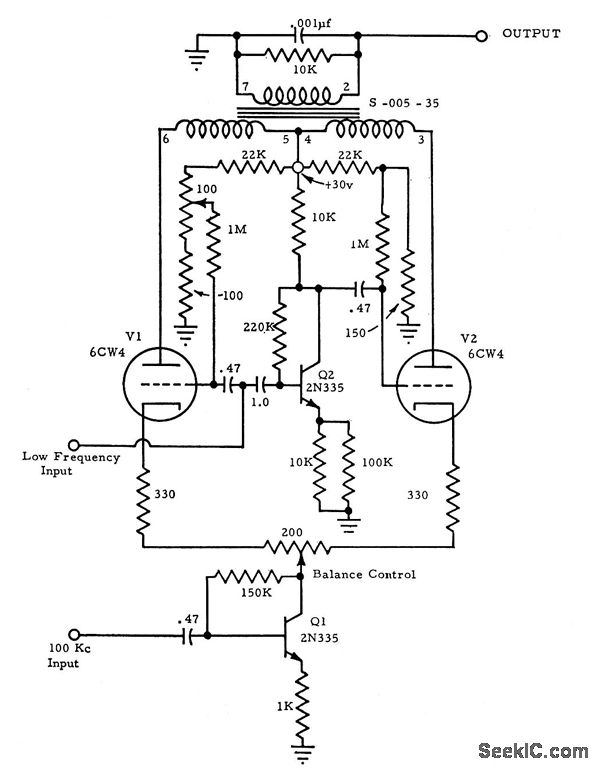
100_KC_HYBRID_BALANCED_MODULATOR Signal_Processing Circuit Diagram
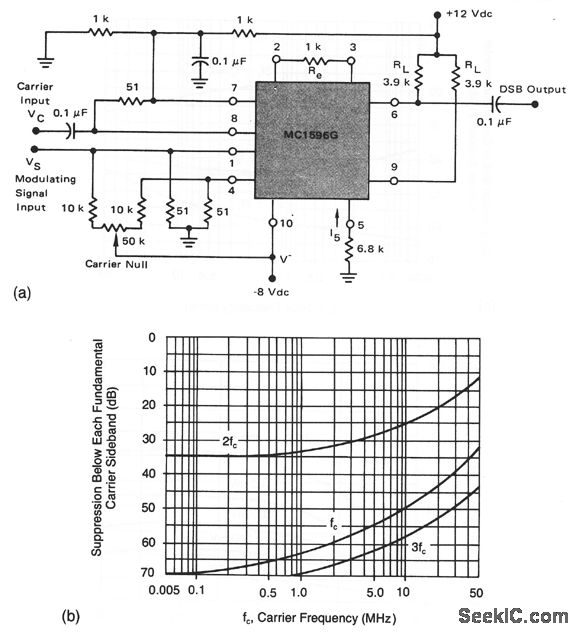
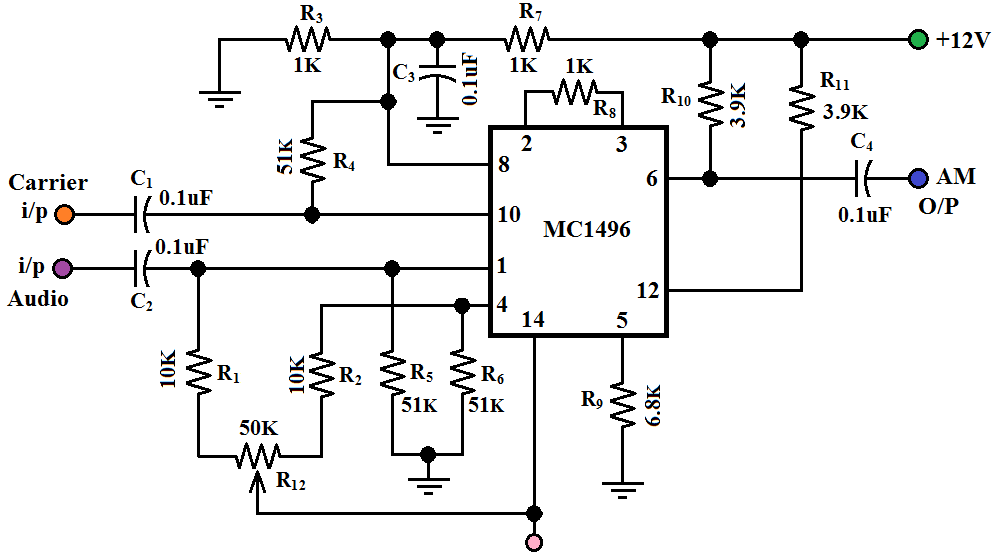
The MC1496 is a monolithic transistor array arranged as a balanced modulator-demodulator. The device takes advantage of the excellent matching qualities of monolithic devices to provide superior carrier and signal rejection. Carrier suppressions of 50dB at 10MHz are typical with no external balancing networks required.
Balanced Modulators
4.1 MC1496 Balanced Modulator/Demodulator The MC1496 is a monolithic transistor array integrated circuit (IC) arranged as a balanced modula-tor/demodulator. It was designed for use where the output voltage is a product of an input voltage (the message) and a switching function (the carrier). Typical applications include double-sideband

(a) Balanced BPSK modulator circuit, (b) S 21 of the modulator using
Download scientific diagram | Balanced Modulator-Demodulator typical Circuit. from publication: Quadrature Phase Shift Keying modulator & demodulator for Wireless Modem | Digital modulation is a.
Balanced_modulator_for_SSB_operation Electrical_Equipment_Circuit
Balanced Modulators/ Demodulators These devices were designed for use where the output voltage is a product of an input voltage (signal) and a switching function (carrier). Typical applications include suppressed carrier and amplitude modulation, synchronous detection, FM detection, phase detection, and chopper applications.
video modulator circuit Video Circuits Next.gr
(G7C01) A balanced modulator is the circuit used to combine signals from the carrier oscillator and speech amplifier and send the result to the filter in a typical single-sideband phone transmitter. (G7C02)
Balance modulator circuit Multisim Live
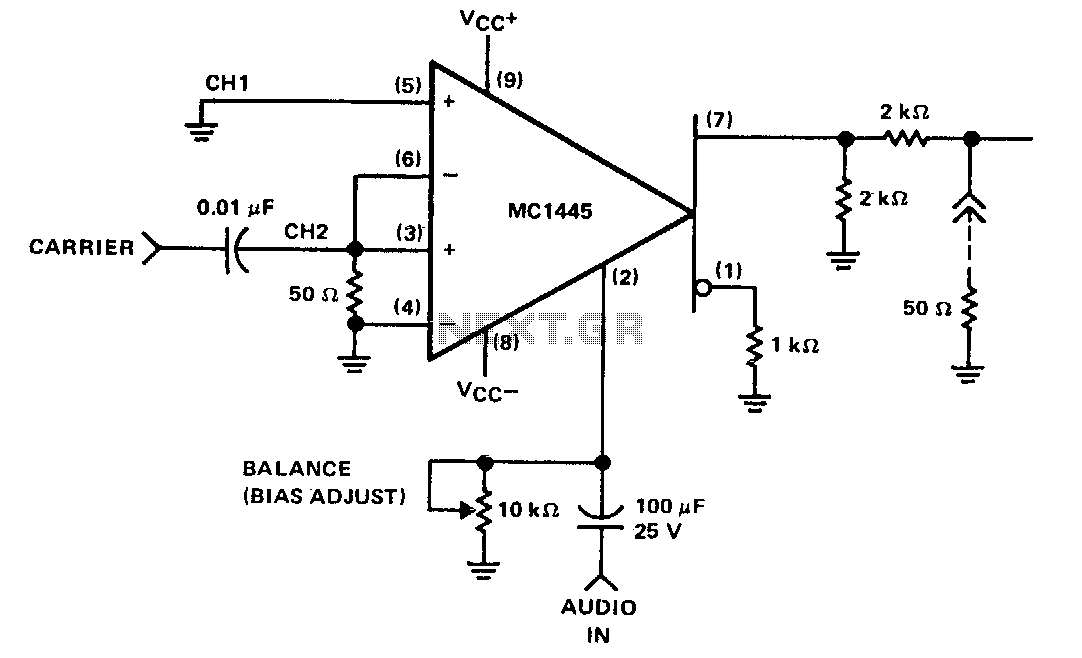
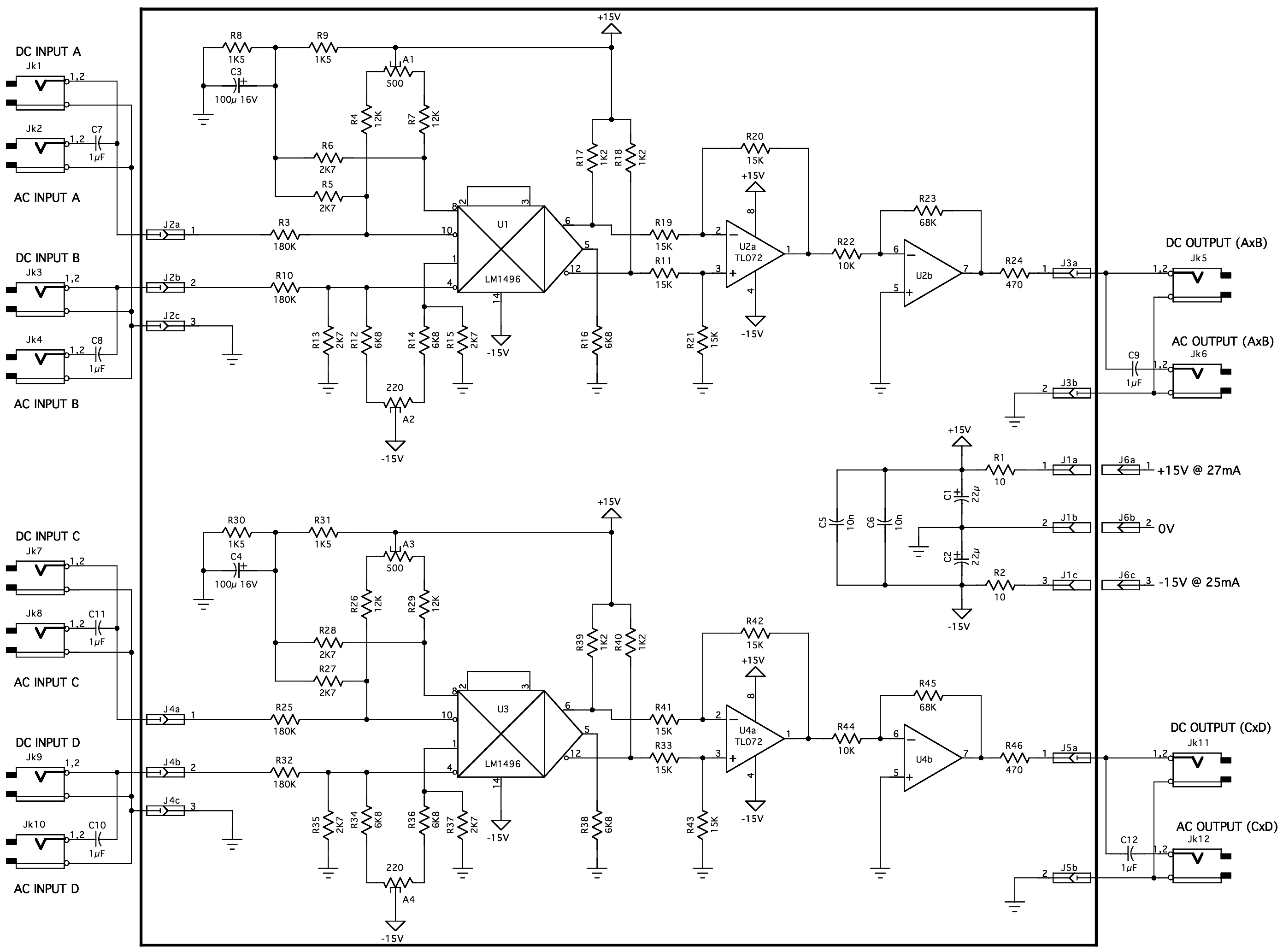
any hybrid or IC balanced modulator/demodulator and is comparable to that of costly signal processing instruments. 3. The op amp format of the AD630 ensures easy implementation of high gain or complex switched feedback functions. The application resistors facilitate the implementation of most common applications with no additional parts. 4.
PPT Figure 41 Balanced ring modulator. PowerPoint Presentation, free
Balanced Modulators/ Demodulators These devices were designed for use where the output voltage is a product of an input voltage (signal) and a switching function (carrier). Typical applications include suppressed carrier and amplitude modulation, synchronous detection, FM detection, phase detection, and chopper applications.
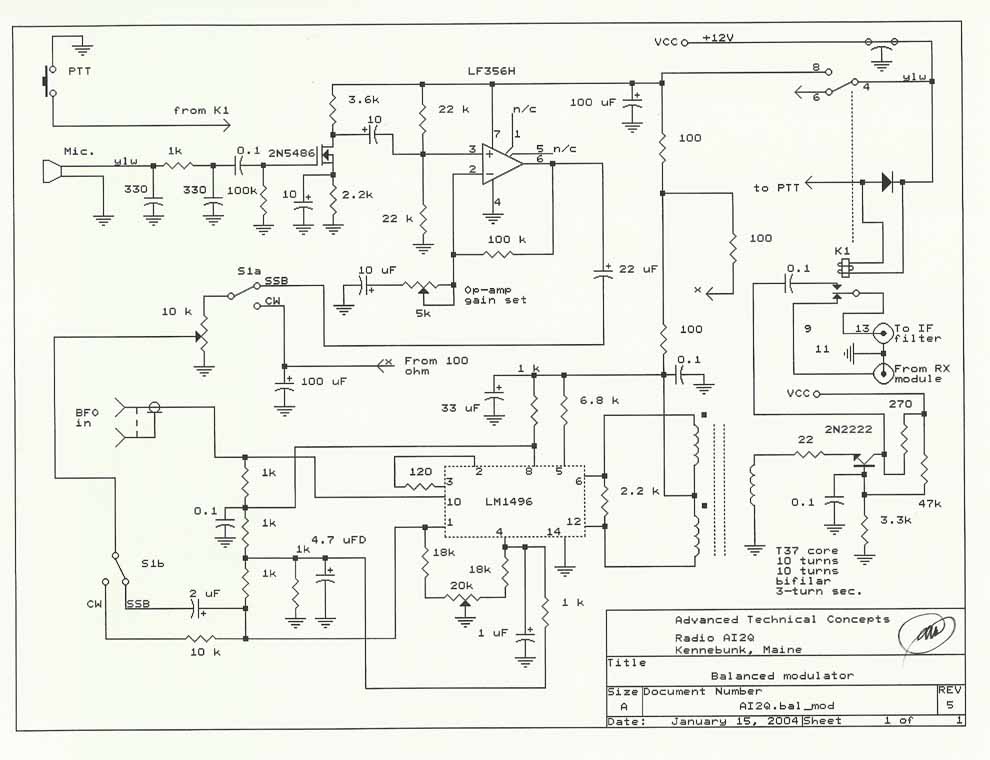
More components are installed on the balanced modulator board.
Balanced modulator consists of two identical AM modulators. These two modulators are arranged in a balanced configuration in order to suppress the carrier signal. Hence, it is called as Balanced modulator. The same carrier signal c(t) = Ac cos(2πfct) c ( t) = A c cos ( 2 π f c t) is applied as one of the inputs to these two AM modulators.

Analog Communication lecture 12 Balanced Modulator and Ring Modulator
Therefore, a balanced modulator may be defined as a circuit in which two non-linear devices are connected in a balanced mode to produce a DSB-SC signal . In this article, we shall discuss a balanced modulator circuit using diodes . Fig.1 shows the balanced modulator using diodes as non-linear device . Fig 1
Circuit Diagram Of Balanced Modulator
Modulators (sometimes called balanced-modulators, doubly-balanced modulators or even on occasions high level mixers) can be viewed as sign-changers. The two inputs, X and Y, generate an output W, which is simply one of these inputs (say, Y) multiplied by just the sign of the other (say, X), that is W = Ysign(X).

Balanced Modulators
Learn more about this topic in Chapter 25 of.http://www.amazon.com/Teach-Yourself-Electricity-Electronics-5th/dp/0071741356/

Balanced Modulator FET circuit Suppression of Carrier DSBSC
General Description The LM1596/LM1496 are doubled balanced modulator-de- modulators which produce an output voltage proportional to the product of an input (signal) voltage and a switching (car- rier) signal.
Balanced Modulators
Excellent gain and carrier suppression can be obtained with this balanced modulator circuit by operating the upper (carrier) differential amplifiers at a saturated level and the lower differential amplifier in a linear mode. The recommended input signal levels are 60 mV rms for the carrier and 300 mV rms for the maximum modulating signal levels.
index.thml
4-4 Balanced Modulators Modulation 4-5 SSB Circuits Chapter Objectives. Explain the relationship of the basic equation for an AM signal to the production of amplitude modulation, mixing, and frequency conversion by a diode or other nonlinear frequency component or circuit.. Describe the operation of diode modulator circuits and diode.